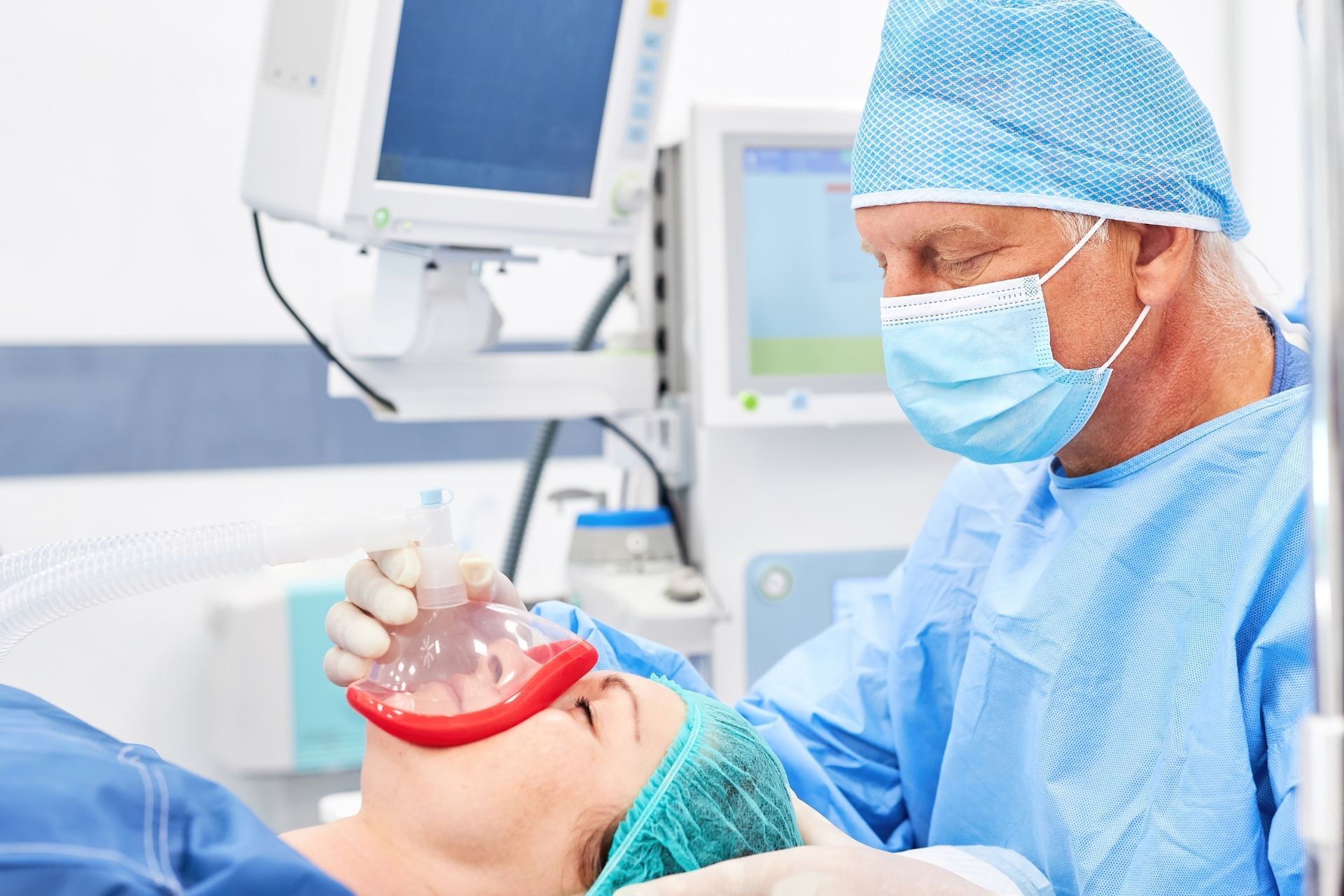
Anesthesia services are provided by healthcare professionals who help patients manage pain and awareness during medical procedures. Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs) monitor the patient’s vital signs while under anesthesia and provide relief from pain and discomfort during and after their procedure. Let’s explore the most common types of anesthesia services used by today’s healthcare professionals.
What Is Anesthesia?
The word “anesthesia” literally translates to “loss of feeling.” In a medical context, it refers to any treatment that prevents a patient from feeling pain or sensation. This is often essential during invasive surgery and certain diagnostic procedures.
Drugs that induce anesthesia are called anesthetics. They include topical compounds containing lidocaine, intravenous (IV) solutions such as propofol, and inhaled gases like isoflurane and nitrous oxide. Medical professionals like CRNAs administer anesthetics and monitor patients while they’re under their effects.
CRNAs provide several distinct types of anesthesia services depending on the amount of sedation needed for a given procedure. Each comes with its own unique benefits and risks, and what works well for one patient may be inadequate for another. Here are some of the most common types of anesthesia services that patients may encounter.
General Anesthesia
General anesthesia is a type of deep sedation that renders a patient unconscious throughout the duration of their procedure. It’s typically administered via inhalation or IV injection, and it works by blocking nerve signals in the brain that control awareness and sensation. General anesthesia also paralyzes the body so that the patient stays still during surgery.
General anesthesia is often used for major surgical procedures, as it allows for a more comfortable experience for both the patient and surgeon. IV drugs like propofol, etomidate, and ketamine are commonly used for general anesthesia. Inhaled drugs like nitrous oxide (NO) and isoflurane are also used as general anesthetics.
Regional Anesthesia
Regional anesthesia numbs a specific area of the body so a patient can undergo a procedure without pain or discomfort. This is typically done with injections around nerves in specific areas, such as the arm, spine, or thigh. Regional anesthesia is generally used for minor surgeries in those areas and can be accompanied by general anesthesia, if necessary.
This type of anesthesia is often used during childbirth to reduce labor pains. It can also be used to reduce pain during major surgeries involving large body parts like hips, legs, or arms having a significant impact on other areas.
Regional anesthetics also come with fewer side effects than general anesthetics due to their more localized action. This tends to reduce the risk of accidental overdose or adverse reactions. Regional anesthesia often involves peripheral nerve blocks, spinal/epidural anesthesia, or IV regional anesthesia.
Local Anesthesia
Local anesthetics (LAs) numb only a small area of the body prior to a procedure. These drugs block nerve signals from passing through to the brain, allowing patients to remain awake but feel no pain. Local anesthetics may also be combined with sedatives to help relax patients before their procedure begins.
This type of anesthesia is often used for biopsies and skin grafts. Local anesthetics can be injected directly into the area being treated or applied topically via creams, sprays, or gels. The effects may last hours to days depending on the medication used and amount administered.
Local anesthetics provide effective pain relief with relatively few long-term side effects, making them a popular choice for minor procedures such as tooth extractions or small surgeries. Some commonly used LAs include lidocaine, procaine (Novocain), and their analogues.
Sedation
Like general anesthesia, conscious sedation or monitored anesthesia care can also affect a patient’s entire body. However, most sedation generally isn’t intended to put a patient to sleep, as they may still be asked to answer some basic questions. It’s often employed to make them feel drowsy and relaxed during a quick procedure such as an eye surgery. CRNAs can achieve distinct levels of sedation based on the unique needs and preferences of their patients.
Ask Us about Anesthesia Services
Anesthesia services come in many forms, from general and regional to topical applications and conscious sedation. However, they all accomplish similar goals by providing safe and effective pain relief during and after surgeries and medical procedures. That’s why CRNAs are some of the most highly trained medical professionals in today’s healthcare industry.
If you have questions or concerns about our distinct types of anesthesia services, then we encourage you to give us a call or reach out online for more information. We’d be happy to answer your questions and help you feel more confident about your upcoming medical procedure.
