Your heart, a tireless pump working faithfully within your chest, is the engine that keeps your entire body running. But just like any engine, it needs regular checkups to ensure it's functioning optimally. A heart stress test has become a cornerstone to evaluating any patient's cardiac functions. Let's dive deep into a test, exploring how they can help you understand your cardiovascular health.
1. What are Heart Stress Tests?
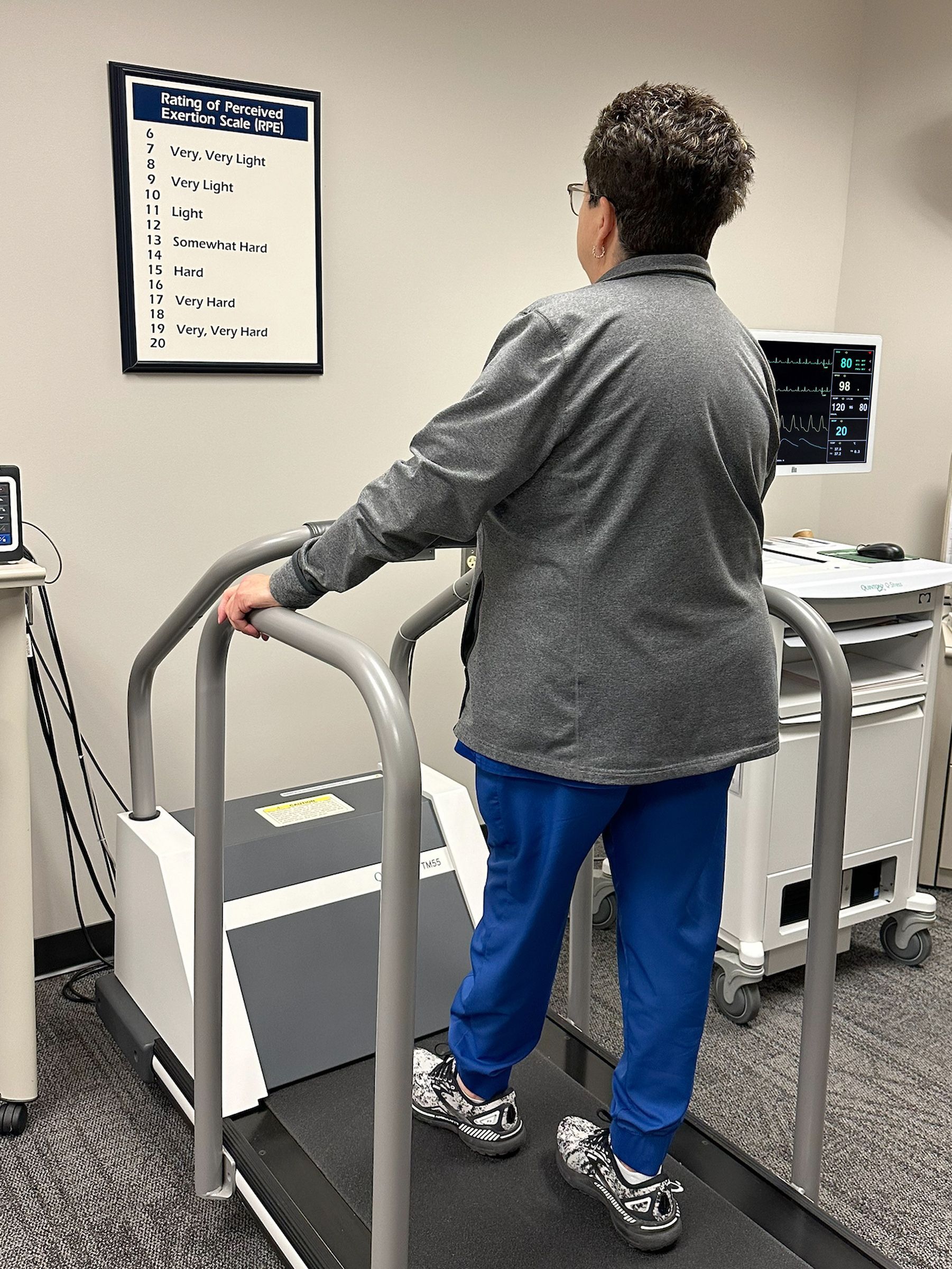
Heart stress tests, also known as exercise stress tests, are non-invasive procedures designed to evaluate your heart's response to physical exertion. By putting your heart under controlled stress, doctors can assess its ability to pump blood effectively, identify potential abnormalities in blood flow, and detect signs of underlying heart conditions. This can help you identify potential causes for future issues like strokes or a heart attack.
Exercise is the preferred method to induce stress during a heart stress test. You'll typically walk on a treadmill with gradually increasing intensity.
2. Different Types of Heart Stress Tests
While their core principles are the same, healthcare providers offer several variations of a heart stress test. Each of these methods provide rich, comprehensive data on different potential problems:
· Electrocardiogram (ECG) Stress Test: The most common test, electrodes are attached to your chest to monitor your heart's electrical activity during rest and exercise. Changes in the ECG pattern, such as ST-segment depression, can suggest potential problems with blood flow to the heart muscle.
· Echocardiogram Stress Test: This combines an ultrasound (echocardiogram) with exercise or pharmacological stress. The ultrasound images your heart at rest and peak stress, allowing doctors to visualize any abnormalities in heart wall movement, which can indicate insufficient blood flow.
· Nuclear Stress Test: This involves injecting a small amount of radioactive material into your bloodstream. Special cameras then capture images of your heart at rest and after stress. Areas with decreased blood flow will appear less radioactive on the scan, potentially revealing blockages in the coronary arteries.
3. The Procedure and What to Expect
The specific procedure for a heart stress test will vary depending on the type chosen by your doctor. Here's a general idea of what to expect:
Before the Test:
· Inform your doctor about any medications you're taking, as some might need to be adjusted before the test.
· Wear comfortable clothing and shoes suitable for exercise.
· You may be advised to avoid eating or drinking heavily for a few hours before the test.
During the Test:
· Electrodes will be attached to your chest to monitor your heart rate and rhythm (ECG).
· Blood pressure will be measured regularly throughout the test.
· In an exercise stress test, you'll gradually start walking on a machine. The intensity will increase progressively until you reach your target heart rate or experience limiting symptoms like chest pain or fatigue.
· Imaging might be performed before, during, and after the stress phase.
4. Interpreting the Results
Following the test, your doctor will analyze the collected data, including your ECG readings, blood pressure measurements, and any imaging results. The interpretation can vary depending on the type of test and your situation.
Some common outcomes include:
· Normal: If your heart rate and rhythm are standard throughout the test, the results should be good. This indicates your heart is functioning well under stress.
· Non-diagnostic: In some cases, the test may not provide a clear answer due to technical limitations or pre-existing conditions. Your doctor might recommend further evaluation with other diagnostic tools.
· Positive: An abnormal ECG pattern, a significant drop in blood pressure during exercise, or evidence of decreased blood flow on imaging suggests potential problems with blood flow to the heart muscle. This could indicate coronary artery disease or other underlying conditions.
Remember that heart stress tests do have limitations:
· False positives: Sometimes, the test might indicate abnormalities even when there's no underlying heart disease. This can be caused by imbalanced electrolytes or medications.
· False negatives: In some cases (particularly if they're mild), the test may overlook existing blockages.
· Exercise limitations: People with certain health conditions like severe arthritis or uncontrolled asthma might not be able to exercise sufficiently for an accurate test.
Book a Heart Stress Test - A Crucial Step in Cardiac Health
The most important takeaway is to discuss your risk factors and concerns with your doctor. They can recommend the most appropriate tests to ensure your cardiovascular health remains a top priority. Our team is dedicated to providing personalized cardiac care and guidance to help you live a long and healthy life. Visit us today in West Point, Nebraska, and get started on rebooting your health journey!
